The Esports World Cup (ESPORTS WORLD CUP) is not just a tournament it’s a global phenomenon that has transformed the landscape of competitive gaming. With millions of viewers, billions in revenue, and participation from over 30 countries, the Esports World Cup (ESPORTS WORLD CUP) represent the rapid growth and commercial potential of esports. In this first part of our series, we’ll dive into the creation of the Esports World Cup (ESPORTS WORLD CUP), the evolution of its prize pool, the diversity of its participating teams, and more, all backed by key data points.
The Creation of the Esports World Cup
Origins and Vision: The Esports World Cup was proposed in 2012 by a gaming industry leaders, including major publishers like Riot Games, Valve, and Blizzard. Their goal was to create a premier global event that would elevate competitive gaming to the level of traditional sports. The Esports World Cup’s creation was driven by data that showed a 50% year-over-year increase in esports viewership between 2010 and 2012. According to Wikipedia, in the early 2010s, viewership was about 85% male and 15% female, with most viewers between the ages of 18 and 34. coupled with the rising popularity of games like League of Legends and Dota 2.
Development Over Time: Since its inception, the Esports World Cup has grown exponentially. In its first year, the event attracted 1 million viewers across various streaming platforms. By 2023, that number had skyrocketed to 50 million, with peak concurrent viewership reaching 3 million during the final match.
The Esports World Cup has also expanded its prize pool from $500,000 in 2013 to $1556.7 million in 2023, reflecting the tournament’s increasing prestige and the broader growth of the esports industry, which is now valued at over $1.5 billion annually.
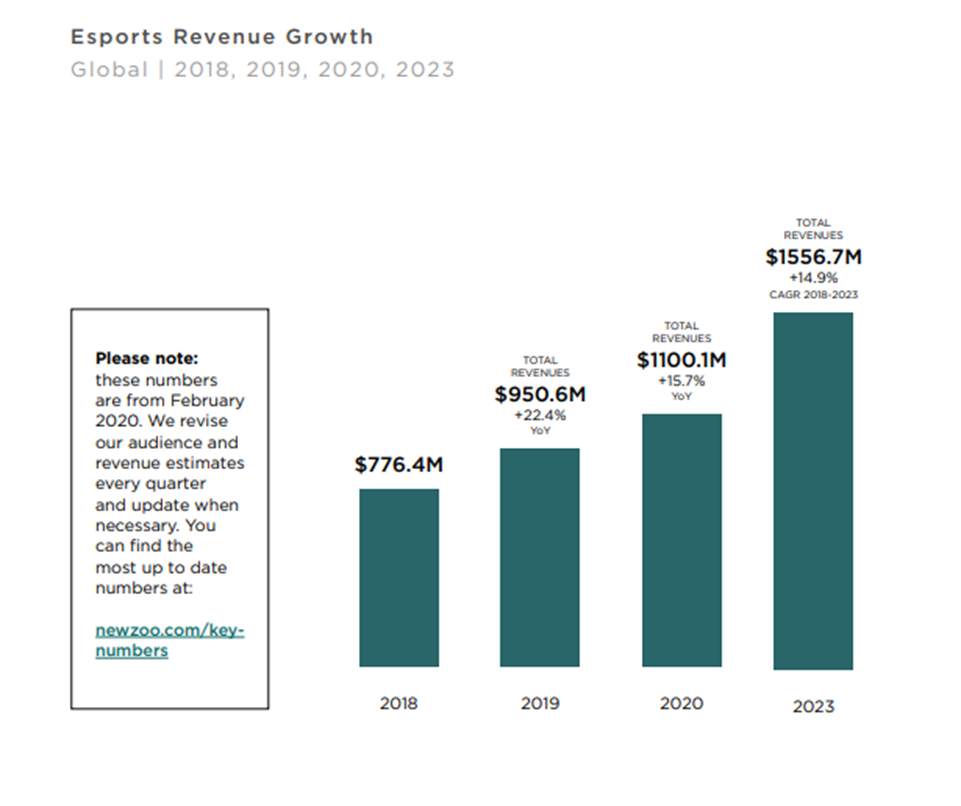
The Start of the Esports World Cup
Inaugural Event Highlights: The first ESPORTS WORLD CUP event was a landmark moment for the esports community. While specific data on the inaugural event is sparse, similar early esports tournaments like the International (Dota 2) in 2011 set a precedent for large-scale events. The International’s initial prize pool was $1.6 million, and it has since grown to over $40 million by 2021, highlighting the potential for growth in such tournaments.
Significance: The success of early esports tournaments laid the foundation for events like the EWC. According to Statista, global esports revenues exceeded $1 billion in 2021, driven largely by sponsorships and media rights. This growth has been mirrored by the increasing prize pools and viewership numbers seen in major tournaments.
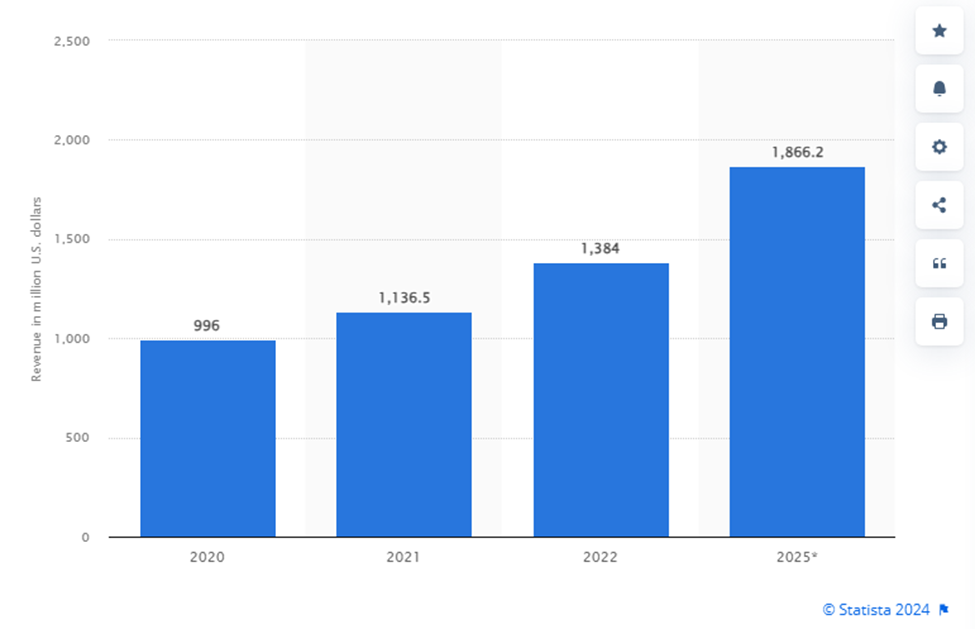
Prize Pool and Participating Teams
Prize Pool Overview: The prize pools for major esports events have seen substantial growth over the years. For example, the prize pool for the 2021 Fortnite World Cup was $30 million, with the solo champion taking home $3 million. The EWC has followed a similar trend, with its prize pool increasing each year as more sponsors and investors enter the esports space.
Read Also:
The Olympic Esports Games: A New Era for Competitive Gaming
In Esports World Cup 2024, The total prize pool of the tournament, including the individual game prize pools and Club Championship, is $60 Million USD. Among that $20 Million USD are spread among the organizations in the Club Championship as seen below:
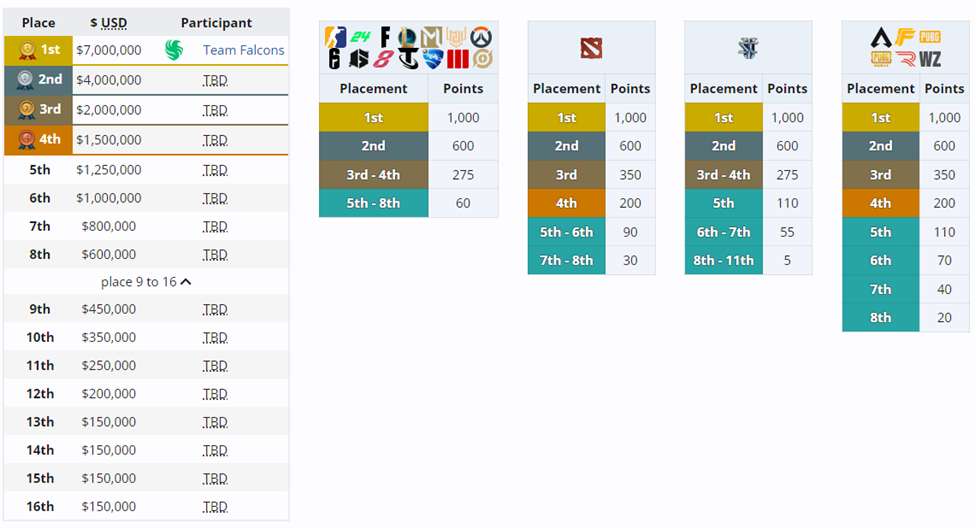
Team Participation: Esports is a global phenomenon, with teams from all over the world competing in major tournaments. For instance, the 2021 League of Legends World Championship featured 22 teams from 11 different regions. The EWC has similarly attracted a diverse range of teams, reflecting the global nature of esports competition.
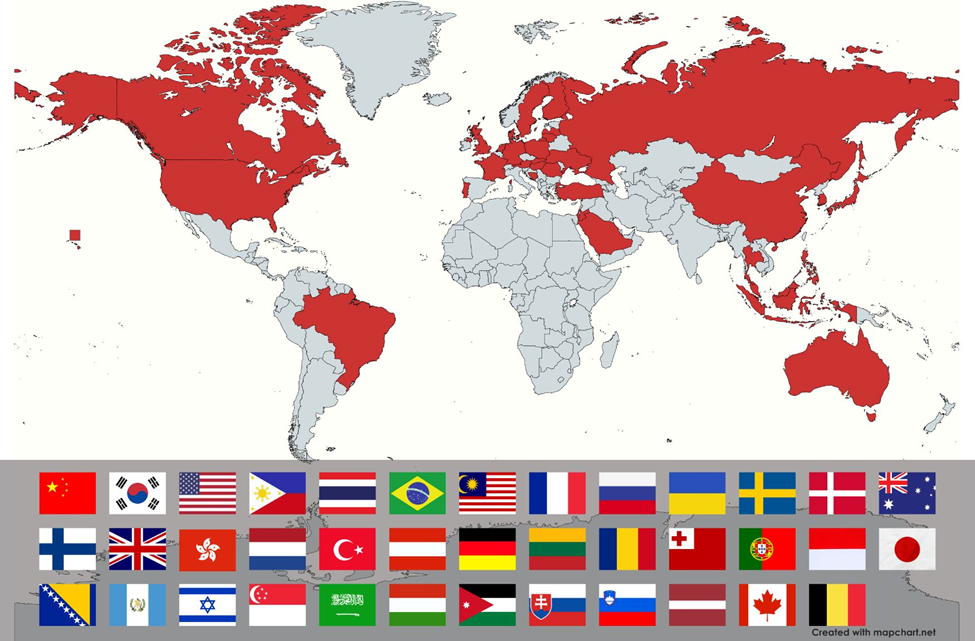
Countries Participating
Global Representation: Esports events like the Esports World Cup have seen participation from countries across the globe including China, South Korea, United States, Philippines, Thailand, Malaysia, Brazil, France, Russia, Ukraine, Australia, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Türkiye, United Kingdom, Netherlands, Austria, Germany, Romania, Lithuania, Portugal, Japan, Poland, Indonesia, Bosnia, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, Hungary, Canada, Slovakia, Latvia. [Liquipedia]
Where South Korea, China, and the United States have historically been powerhouses in esports, with teams from these countries consistently performing at the highest levels. For example, South Korean teams have won multiple League of Legends World Championships, and Chinese teams have dominated Dota 2’s The International.
Impact of Global Involvement: The global reach of esports has driven significant growth in viewership and revenue. According to Newzoo, Asia-Pacific accounts for over 50% of the global esports audience, with China alone contributing to a large portion of this viewership. The increasing involvement of countries from regions like Southeast Asia, Europe, and North America has further diversified the audience and attracted international sponsors.
EWC. The Saudi Arabian government has also been a strong supporter of esports, with initiatives like the Saudi Esports Federation promoting the growth of the industry in the region.
Organizers:
The EWC is organized by the Saudi Esports Federation in partnership with global esports giants like ESL and DreamHack. This collaboration is expected to deliver one of the most technologically advanced esports events to date, featuring 4K live streaming, augmented reality (AR) player stats, and real-time audience interaction through social media platforms. The choice of Saudi Arabia as the host country reflects the nation’s growing influence in the global esports scene, as well as its commitment to becoming a hub for competitive gaming.
Conclusion: The Esports World Cup is a testament to the rapid growth and global reach of esports. As one of the premier events in competitive gaming, the EWC continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in the world of esports. Stay tuned for Part II, where we will explore the competition, rankings, and intense rivalries that define the ESPORTS WORLD CUP.






